Chest pain can be a distressing symptom that can have a variety of causes. And it’s crucial to determine the underlying source to provide appropriate treatment. While cardiac issues are common, not all chest pain is related to the heart. In some cases, misalignments or tension in the chest area can lead to discomfort and pain. That may mimic cardiac-related symptoms. It is called non-cardiac chest pain.
Chiropractic offers a non-invasive approach to solving musculoskeletal problems. These problems can contribute to chest pain. Chiropractors often focus on the spine and surrounding structures. In this way, they seek to restore proper alignment. Chiropractic care also helps relieve stress and improve general well-being. Chiropractor chest adjustment can target misalignments and imbalances in the thoracic spine, ribcage, and associated muscles.
We will explore the causes and symptoms of non-cardiac chest pain. We will also talk about the role of chiropractic in correcting the chest and relieving chest pain.
What causes Non-Cardiac Chest Pain?
Extra-cardiac chest discomfort can be surprising to the patient. Its origin lies outside the realm of heart-related problems. Instead, several alternative factors may contribute to this discomfort.
Here are some common causes of non-cardiac thorax pain:
- Problems of the musculoskeletal system. Poor posture or physical injury can lead to musculoskeletal problems. These problems manifest themselves in the form of discomfort in the breastbone.
- Costochondritis. Inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum is known as costochondritis. This condition is often provoked by trauma, infection, or excessive coughing.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Malfunctions of the digestive system can cause discomfort that resembles heart symptoms.
- Psychological factors. The mind-body connection plays an essential role in human health. Muscle tension due to stress can contribute to non-cardiac chest pain.
- Respiratory diseases. Asthma or pneumonia can cause thorax discomfort. It occurs due to inflammation or irritation of the respiratory tract and lungs.
- Various reasons. Non-ischemic chest soreness can also arise from a variety of sources. It can be problems with the gallbladder, nerves, or a side reaction to certain medications.
Determining the underlying cause of chest discomfort requires a thorough examination. Only a medical professional can diagnose accurately and prescribe drugs or sternum adjustment.
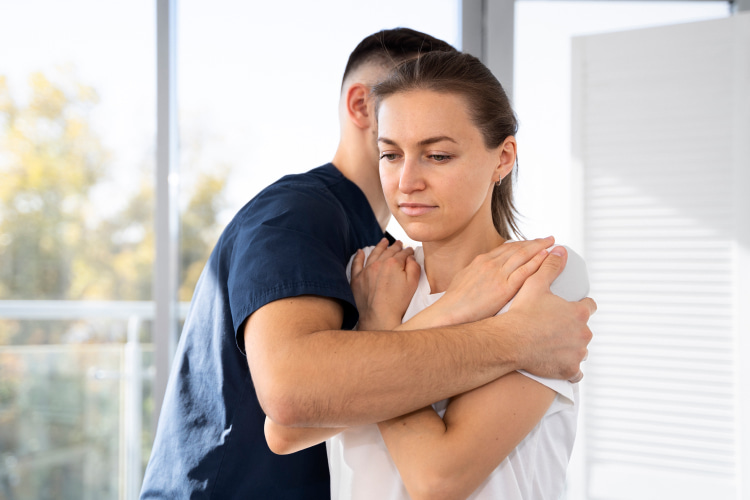

Chiropractic Care for Non-Cardiac Chest Pain
Manual therapy can be a practical approach to managing non-ischemic discomfort. Chiropractors aim to address underlying issues that may contribute to chest soreness. They focus on the musculoskeletal system and provide relief through various techniques.
Chiropractic chest pain can help you improve your health. This therapy does not include any drugs. Specialists work only with your body. They help eliminate tension and clamps in the thorax with the help of various movements. Manual therapy can also help balance your posture. Often it is the curved spine that causes pain in the breastbone.
Chiropractic care offers a non-invasive and alternative approach to addressing the underlying causes of extra-cardiac thorax discomfort. Manual therapy focuses on the musculoskeletal system. This provides relief and improves the overall function of the breastbone.
Chiropractic care can help you relieve chest pain and improve musculoskeletal health. To understand how it works, you should understand this holistic approach and its potential benefits.
Here are some common chiropractic treatments used for non-ischemic chest discomfort:
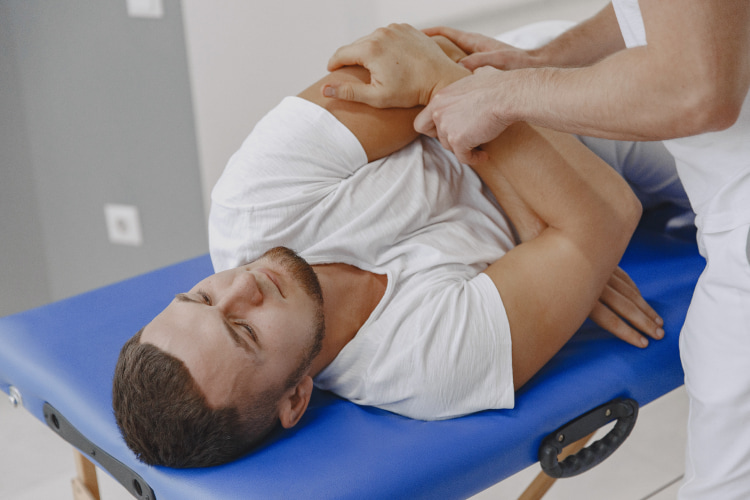
Chiropractor chest adjustment
Chiropractors use manual adjustments to realign the spine and restore proper joint function. For non-cardiac pain, they may target the thoracic spine and ribs. A specialist will help you reduce tension, muscle imbalances and improve chest mechanics. This change aims to restore proper mobility, and function to the thoracic region. It can also help alleviate musculoskeletal issues.
Soft tissue therapy
Chiropractors often use methods of influencing soft tissues. It can be massage, myofascial release, or trigger point therapy. These techniques help relieve tension, reduce inflammation, and promote relaxation in the chest. Soft tissue therapy can be used to address muscle imbalances.
Therapeutic exercises
Chiropractors can prescribe special exercises and stretches. These exercises help sternum adjustment, strengthen the chest muscles and promote flexibility. They can also help improve posture and reduce muscle imbalances.
Postural education and lifestyle recommendations
Poor posture can contribute to chest pain due to excessive strain on this body part. Chiropractors often teach patients about proper posture. They provide guidance on how to exercise and prevent future problems. Therapists also often offer lifestyle advice. It may include advice on diet, stress management, and other self-care strategies.
Research and Evidence
Сhiropractor chest adjustment is an effective method of treating non-cardiac chest pain. Currently, there are some studies that confirm the effectiveness of such methods:
- Chiropractic management of chronic chest pain using mechanical force, manually assisted short-lever adjusting procedures. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of chiropractic care for non-cardiac chest pain. The patient received manually assisted short-lever chiropractic adjustment of the thoracic spine. The patient responded favorably to the intervention, obtaining prompt relief from his symptoms. Sustained chiropractic care rendered over 14 weeks resulted in complete resolution of the patient’s.
Learn: Chiropractic Management of Chronic Chest Pain
- Clinical presentation and chiropractic treatment of Tietze syndrome: A 34-year-old female with left-sided chest pain. Tietze’s syndrome is a differential diagnosis for chest pains of musculoskeletal origin. Research has shown that chiropractic treatment may be possible in improving the condition.
Learn: Chiropractic Treatment of Tietze Syndrome
- Chiropractic Treatment vs Self-Management in Patients With Acute Chest Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Patients Without Acute Coronary Syndrome. Both groups experienced a reduction in pain and positive changes. Significant differences between groups were observed in favor of chiropractic. The results suggest that chiropractic care may be beneficial. Chiropractic chest pain helps patients feel better. But further research on this is needed.
Learn: Chiropractic Treatment vs Self-Management With Chest Pain
These studies provide preliminary evidence supporting the effectiveness of manual therapy. This method has shown good results in the treatment of non-cardiac chest pain. However, it is important to note that individual response to treatment may vary. If you have chest pain that is not related to the heart, it is better to consult a doctor. Only a professional will determine the most appropriate approach to treatment for each individual case.
FAQ
How do you relieve noncardiac chest pain?
First of all, you need to seek a medical examination. The doctor can advise you on relaxation techniques or correcting your posture.
What is non-cardiac chest pain?
This is pain or discomfort that is not related to the heart. Various factors can cause it. The leading causes are musculoskeletal problems or other non-cardiac sources.
Is chiropractic care safe for chest adjustments?
Yes, manual therapy for breast correction is generally considered safe. It is important that it is performed by a trained and licensed chiropractor.


Related posts
Today is an era dominated by digital conveniences and desk-bound occupations. So, the effects of a sedentary lifestyle have emerged as a pervasive concern.
Our guide aims to equip people with the knowledge to understand the intricacies of internal injuries. They are arising as a result of car accidents. Join us on this informative trip.
Beyond merely treating injuries, chiropractors work to enhance the body's biomechanics. It allows sportsmen to move more potently and reduces the risk of future injuries.